Do Vaccines Cause Autoimmune Disease In Dogs are usually safe and effective, but there is always a chance of adverse effects with any medical procedure. Dog autoimmune illnesses are complicated conditions with many potential causes, including environmental variables and genetic predispositions. Although they are uncommon, adverse effects are possible.
Table of Contents
Although it is exceedingly rare, immunizations may occasionally cause an inflammatory reaction that results in autoimmune disorders.
The Link Between Vaccines and Autoimmune Diseases
The veterinary profession is still researching and debating the connection between immunizations and autoimmune illnesses, especially in dogs. Although vaccinations are effective at preventing infectious diseases, some people are concerned that they may occasionally be linked to autoimmune disorders. When the immune system unintentionally attacks and targets the body’s tissues, autoimmune disorders result.

Vaccines for dogs are intended to boost the immune system’s ability to mount defenses against particular diseases. Vaccines are thought to be safe overall, but they could cause an immune response that isn’t right, which could result in autoimmune diseases. It’s crucial to remember that there isn’t much chance that receiving a vaccination may cause you to acquire an autoimmune disease.
Recognizing Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases in Dogs
Identifying the signs of autoimmune illnesses in dogs is essential to provide early intervention and successful treatment. When the immune system unintentionally targets the body’s cells, it can result in autoimmune disorders and other health problems. Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus are common autoimmune disorders in dogs.
Dogs with autoimmune disorders may exhibit a variety of symptoms, including:
Lethargy: In dogs, lethargy is a worrying indicator of possible health problems. An ordinarily energetic dog exhibiting lethargy may suffer from pain, disease, or psychological discomfort. Infections, dietary deficits, or underlying medical issues are common causes.
Joint discomfort: Canine joint pain is common, particularly in larger breeds or older dogs. Injuries, hip dysplasia, and arthritis can cause pain and limited movement. The symptoms include stiffness, hesitancy to move, and limping.
Dog skin issues can take many forms, ranging from flakiness and blisters to itching and redness. Allergies, parasites, infections, or underlying medical conditions are frequently to blame. An issue could be indicated by licking, scratching, or changes in coat quality.
Changes in appetite: Dogs with autoimmune disorders may experience disturbances in their regular eating habits, which may result in changes in appetite. Depending on their autoimmune disease, affected dogs may become less or more hungry. Due to decreased food intake, inflammatory bowel disease, and autoimmune thyroiditis can cause weight loss.
Owners need to be on the lookout for persistent symptoms and seek veterinary care. Appropriate treatment measures must be implemented as soon as possible to improve the quality of life for afflicted canines.
Dog Aggression After Vaccine
There is insufficient proof to conclude that vaccinations cause canine autoimmune disorders directly. Nonetheless, a few dog owners have noted that their dogs have become more aggressive after immunizations. It is important to remember that most dogs do not become violent because of their vaccines and that these instances are extremely uncommon.

Given the factors that might influence aggression, including heredity, environment, and individual temperament, the relationship between dog aggression and vaccinations may be coincidental. Furthermore, tension or discomfort related to the injection procedure may cause post-vaccination behavioral changes rather than the vaccine itself.
Treatment For Do Vaccines Cause Autoimmune Disease In Dogs
Dogs with autoimmune illnesses are treated with an emphasis on symptom management and immunological response suppression to stop further damage. Using immunosuppressive medications, such as corticosteroids or other immune-modulating pharmaceuticals, is a common strategy. These drugs aid in reducing inflammation and the hyperactive immune response that autoimmune diseases are known for.
Although vaccinations are pretty effective at preventing many infectious diseases, some claim that some of the adjuvants or components in vaccines may cause an immune response that is not optimal, which could cause autoimmune problems in those who are vulnerable.
Can Autoimmune Disease Kill a Dog?
Dogs with autoimmune illnesses do have significant health hazards, some of which can be fatal. These disorders develop when the immune system unintentionally attacks the body’s tissues, causing inflammation and tissue damage. Although autoimmune diseases can be deadly in and of themselves, there is continuous discussion and research in the veterinary field regarding the potential link between vaccinations and autoimmune diseases in dogs.
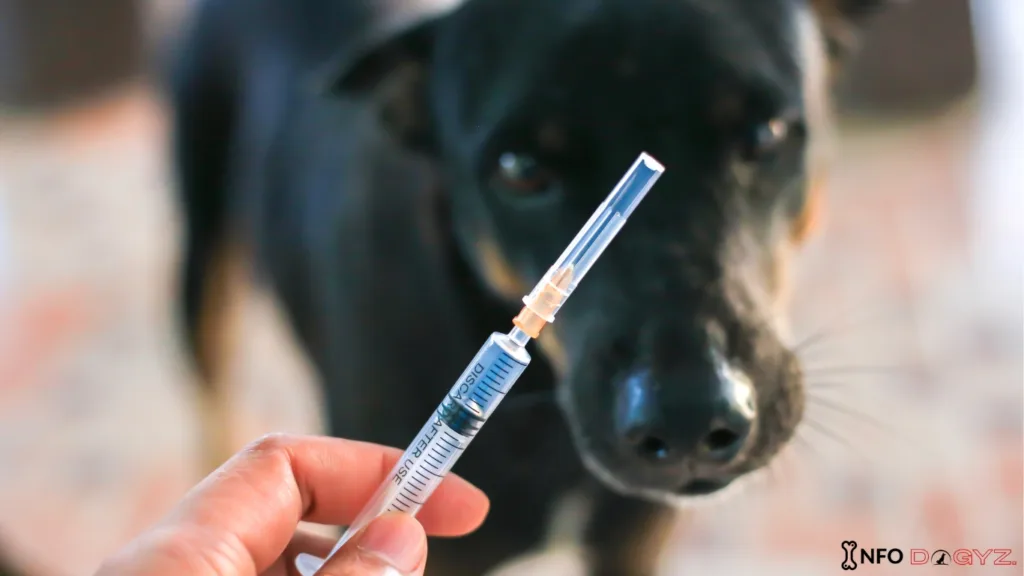
While vaccinations are an essential tool in the fight against infectious illnesses, there is concern that they could inadvertently set off an immune response that could eventually lead to the onset of autoimmune disorders. It is important to remember that the benefits of avoiding potentially fatal illnesses far outweigh the danger of a dog acquiring an autoimmune condition due to vaccination.
Conclusion
In the complex landscape of canine health, the question remains, Do Vaccines Cause Autoimmune Disease In Dogs?. By making your way through the professional judgments, firsthand accounts, and scientific discoveries offered in this extensive guide. A summary of the most important lessons learned from investigating the connection between vaccinations and autoimmune disorders in dogs. Finding the balance between reducing potential hazards and safeguarding our furry friends is essential to responsible pet ownership.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: Do dogs who receive immunizations develop autoimmune diseases?
A: Revealing the reality of this widely held worry and the viewpoint of science.
Q: What are the early indicators of canine autoimmune diseases?
A:Early symptom recognition allows for prompt intervention and therapy.
Q: Are some breeds more susceptible to autoimmune illnesses linked to vaccinations?
A: Determining whether and why particular breeds are more vulnerable.
Q: Is titer testing a trustworthy substitute for routine immunizations?
A: Recognizing the mutual benefits of conventional immunizations and holistic approaches.
Q: When vaccinating my dog, what should I discuss with my veterinarian?
A: Essential questions to ask your veterinarian to make well-informed choices regarding the health of your pet